- News
- Mike’s Blog
- CLIC News Roundup
- CTSA Ansible
In today’s high-tech world, researchers are capturing and analyzing an abundance of data to improve human health. But this data is often difficult to share and use broadly because it’s captured in a variety of forms using a variety of systems. The lack of interoperability — the ability to share and use data across multiple systems — could lead to missed discoveries.
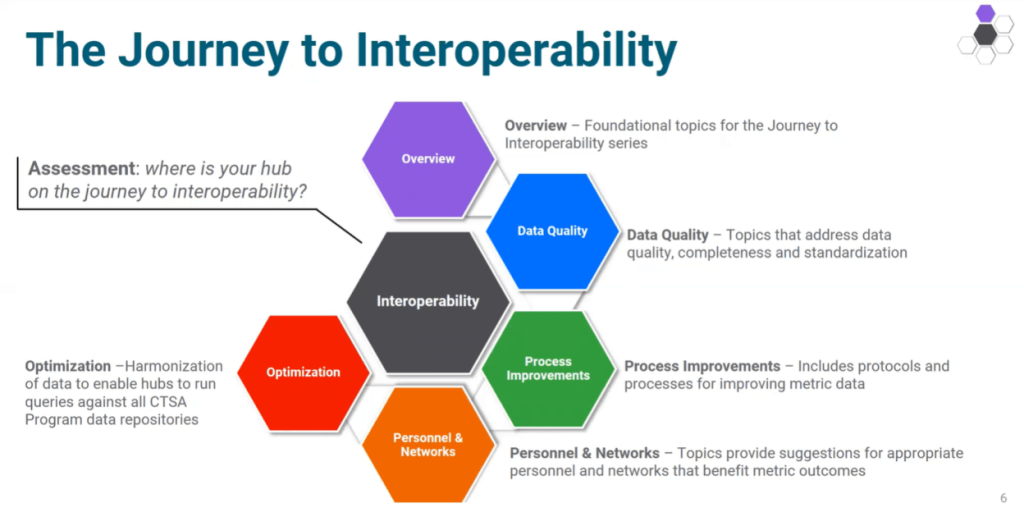
To bolster data interoperability across the CTSA Program, the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) implemented the Informatics Common Metric, which measures several aspects of hubs’ informatics prowess, including interoperability. This year, the Insights to Inspire (I2I) program, which the Center for Leading Innovation and Collaboration (CLIC) administered, focused on informatics. Like in past years, the I2I campaign, Informatics: The Journey to Interoperability, aims to foster innovation, increase collaboration across the consortium and give hubs the tools they need to improve.
“The informatics metric is somewhat unique in that, unlike many of the other metrics, this one is more of a foundational metric,” said Dr. Ken Gersing, M.D., the director of informatics at NCATS. “If we don’t have good data…if we can’t trust the answers, we really can’t function.”
In the I2I webcast Introduction to Informatics, Gersing said the informatics metric provides a roadmap for hubs to see where they stand right now and where they can go in the future. It also makes it easier for hubs to share data with each other.
“This is how we’re going to speak to each other and how we’re going to work together as a network,” he said. “That will show our potential better than anything.”
Before hubs can reach data interoperability, they must have a strong informatics foundation. That’s why this year’s I2I campaign started with the basics, like understanding the language of informatics and using maturity models to assess where informatics programs or individual projects are in their development.
In the Language of Informatics webcast, Dr. Adam Wilcox, professor of biomedical informatics and medical education at the University of Washington (UW), and chief analytics officer at UW Medicine, starts at square one: defining the jargon of informatics. From the term “informatics” itself to “data provenance” and “common data model,” Dr. Wilcox goes in-depth on what these terms mean for the informatics novice.
Wilcox also explains in the webcast Introduction to Maturity Models how institutions can use maturity models to improve their informatics capabilities.
Maturity models are a set of indicators or stages that represent progress in a particular domain or discipline. They show institutions what they need to improve upon and how they can move forward.
“That stage concept is important,” Wilcox said. “Over time, you mature and advance through the stages.”
Though there are a lot of different maturity models, Wilcox said, they can all help improve organizations by enhancing organizational learning, allowing an efficient assessment of practices and giving well-defined pathways to achieve value. They “help you understand how to assess and figure out how to get where you want to go,” Wilcox said.
Wilcox recommends that CTSA Program hubs assess their current research informatics capacity using a Center for Data to Health’s tool for assessing maturity models.
After mastering the basics, institutions can work toward reaching data interoperability. The webcast Importance of Interoperability discusses how the National COVID Cohort Collaborative is a real-world example of how interoperability can increase collaboration between institutions and help researchers answer pressing questions more quickly.
N3C aggregates and uses COVID-19 clinical data to answer questions about the effects of COVID-19 in the U.S. population. Its Data Enclave securely stores clinical data from over six million Americans — over two million of whom have had confirmed cases of COVID-19.
Thanks to an enormous data extraction, aggregation and harmonization effort, N3C data are transparent and easily shared and used by researchers across the country, fostering discoveries and improving public health.
Watch all 12 Insights to Inspire webcasts on the CLIC website.